WhiteBox Part 1: Computer Vision
The White Box Project is a project that introduces many ways to solve the part of the black box of machine learning. In this part, i’ve introduced and experimented with ways to interpret and evaluate models in the field of image.
I shared Korean versions for each reference to study methodology and English. Please refer to the reference.
참고자료별로 영어공부겸 한국어로 번역한 자료가 있습니다.
1. Requirements
pytorch >= 1.2.0
torchvision == 0.4.0
2. How to Run
Model Train
python main.py --train --target=['mnist','cifar10'] --attention=['CAM','CBAM','RAN','WARN']
Model Selectivity Evaluation
python main.py --eval=selectivity --target=['mnist','cifar10'] --method=['VGB','IB','DeconvNet','IG','GB','GC','GBGC']
Model ROAR & KAR Evaluation
For ROAR and KAR, the saliency map of each attribution methods that you want to evaluate must be saved prior to the evaluation.
python main.py --eval=['ROAR','KAR'] --target=['mnist','cifar10'] --method=['VGB','IB','DeconvNet','IG','GB','GC','GBGC']
3. Dataset
- MNIST
- CIFAR-10
4. Models
Simple CNN Model
- 3 convolution layers networks (Simple CNN)
Attention Modules
- Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) [1]
Attention Models
- Class Activation Methods (CAM) [2]
- Residual Attention Network (RAN) [3]
- Wide Attention Residual Network (WARN) [4]
5. Interpretable Methods
Attribution Methods
- Vanilla Backpropagation (VBP) [Notebook]
- Input x Backpropagation (IB) [Notebook]
- DeconvNet [5] [Notebook]
- Guided Backpropagation (GB) [6] [Notebook]
- Integrated Gradients (IG) [7] [Notebook]
- Grad-CAM (GC) [8] [Notebook]
- Guided Grad-CAM (GB-GC) [8] [Notebook]
Ensemble Methods
- SmoothGrad (SG) [9]
- SmoothGrad-Squared (SG-SQ) [10]
- SmoothGrad-VAR (SG-VAR) [10]
6. Evaluation
- Coherence
- Selectivity
- Remove and Retrain (ROAR) [10]
- Keep and Retrain (KAR) [10]
7. Experiments
7.1. Model Architecture & Performance
More information on the model architectures and learning process can be found on the notebook : [Evaluation] - Model Performance
| MNIST | Number of Parameters | 0 - zero | 1 - one | 2 - two | 3 - three | 4 - four | 5 - five | 6 - six | 7 - seven | 8 - eight | 9 - nine | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple CNN | 1284042 | 0.998 | 0.995 | 0.995 | 0.995 | 0.993 | 0.990 | 0.986 | 0.989 | 0.996 | 0.985 | 0.992 |
| Simple CNN + CAM | 1285332 | 0.994 | 0.995 | 0.989 | 0.995 | 0.988 | 0.988 | 0.993 | 0.981 | 0.986 | 0.977 | 0.988 |
| Simple CNN + CBAM | 1288561 | 0.998 | 0.995 | 0.992 | 0.996 | 0.990 | 0.990 | 0.990 | 0.991 | 0.995 | 0.989 | 0.993 |
| RAN | 27987466 | 0.997 | 0.998 | 0.996 | 0.995 | 0.989 | 0.991 | 0.996 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.990 | 0.994 |
| CIFAR10 | Number of Parameters | airplane | automobile | bird | cat | deer | dog | frog | horse | ship | truck | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple CNN | 2202122 | 0.872 | 0.905 | 0.692 | 0.731 | 0.843 | 0.660 | 0.904 | 0.864 | 0.860 | 0.916 | 0.825 |
| Simple CNN + CAM | 2203412 | 0.760 | 0.896 | 0.585 | 0.477 | 0.752 | 0.804 | 0.769 | 0.711 | 0.837 | 0.862 | 0.745 |
| Simple CNN + CBAM | 2206641 | 0.858 | 0.945 | 0.749 | 0.685 | 0.790 | 0.761 | 0.826 | 0.798 | 0.873 | 0.896 | 0.818 |
| RAN | 27990666 | 0.843 | 0.882 | 0.758 | 0.701 | 0.776 | 0.586 | 0.916 | 0.844 | 0.924 | 0.873 | 0.810 |
8. Evaluation Results
8.1. Saliency maps by Layers
Saliency maps by layers : CIFAR10

Top : SimpleCNN / Bottom : SimpleCNN + CBAM
Saliency maps of RAN by layers : CIFAR10
.jpg?raw=true)
8.2. Coherence
[Notebook]
Coherence is a qualitative evaluation method that shows the importance of images. Attributions should fall on discriminative features (e.g. the object of interest).
Saliency maps of each attribution methods applied to the Simple CNN : MNIST & CIFAR10


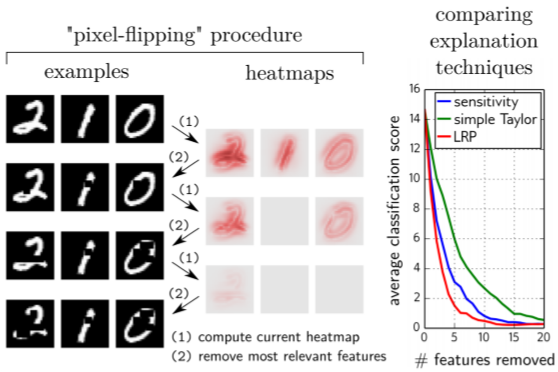
8.3. Selectivity
[Notebook]
Selecticity is a method for quantitative evaluation of the attribution methods. The evaluation method is largely divided into two courses. First, the feature map for the image is created and the most influential part is deleted from the image. The second is to create the feature map again with the modified image and repeat the first process.
As a result, IB, GB and GB-GC were the most likely attribution methods to degrade the performance of models for the two datasets.
MNIST

CIFAR-10

8.4. ROAR/KAR
ROAR/KAR is a method for quantitative evaluation of the attribution methods that how the performance of the classifier changes as features are removed based on the attribution method.
- ROAR : replace N% of pixels estimated to be most important [Notebook]
- KAR : replace N% of pixels estimated to be least important
- Retrain Model and measure change in test accuracy
ROAR and KAR graph of saliency maps of each attribution methods applied to the Simple CNN


ROAR and KAR graph of saliency maps extracted by Grad-CAM for each model
.jpg?raw=true)
.jpg?raw=true)
9. Reference
-
[1] Wang, F., Jiang, M., Qian, C., Yang, S., Li, C., Zhang, H., … & Tang, X. (2017). Residual attention network for image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 3156-3164). [Paper]
-
[2] Zhou, B., Khosla, A., Lapedriza, A., Oliva, A., & Torralba, A. (2016). Learning deep features for discriminative localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 2921-2929). [Paper]
-
[3] Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J. Y., & So Kweon, I. (2018). Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (pp. 3-19). [Paper]
-
[4] Rodríguez, P., Gonfaus, J. M., Cucurull, G., XavierRoca, F., & Gonzalez, J. (2018). Attend and rectify: a gated attention mechanism for fine-grained recovery. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (pp. 349-364). [Paper]
-
[5] Zeiler, M. D., & Fergus, R. (2014, September). Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 818-833). Springer, Cham. [Paper] [Korean version]
-
[6] Springenberg, J. T., Dosovitskiy, A., Brox, T., & Riedmiller, M. (2014). Striving for simplicity: The all convolutional net. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6806. [Paper]
-
[7] Sundararajan, M., Taly, A., & Yan, Q. (2017, August). Axiomatic attribution for deep networks. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning-Volume 70 (pp. 3319-3328). JMLR. org. [Paper]
-
[8] Selvaraju, R. R., Cogswell, M., Das, A., Vedantam, R., Parikh, D., & Batra, D. (2017). Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 618-626). [Paper] [Korean version]
-
[9] Smilkov, D., Thorat, N., Kim, B., Viégas, F., & Wattenberg, M. (2017). Smoothgrad: removing noise by adding noise. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.03825. [Paper] [Korean version]
-
[10] Hooker, S., Erhan, D., Kindermans, P. J., & Kim, B. (2018). Evaluating feature importance estimates. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.10758. [Paper] [Korean version]